Revised: 06/20/2024
Petty Cash Accounts Process |
|
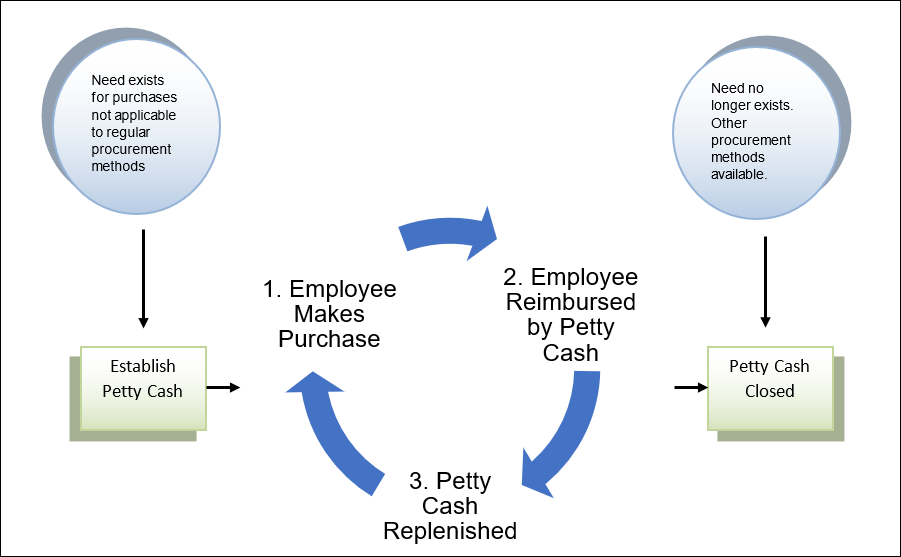
All petty cash accounts authorized by OBM operate using the imprest system. The imprest system is a type of financial accounting system, and is most commonly used for petty cash. An imprest system has the following essential features:
As an example of the imprest system, when the petty cash account balance gets low, the custodian submits the receipt(s) for replenishment on a voucher. If the account is established at $100, and assuming the receipt(s) add up to $80, a replenishment voucher is created in OAKS FIN. Once approved, an $80 Warrant (Check) is issued. When the Warrant (Check) is cashed, the custodian again has cash at the authorized amount of $100.
An agency Director can request OBM to authorize the establishment of a petty cash account. This can be for one of the following types of accounts:
General Use account for routine, small incidental purchases
Special Use account when the need for confidentiality, security or other unique applications require uncommon exceptions to this guidance be granted.
As expenditures are made, the custodian of the fund will reimburse employees who furnish a receipt/invoice. At any given time the total of the items below must equal the authorized amount of the account.
Checkbook balance (if applicable)
Cash on hand
Receipts on hand
Outstanding vouchers
Uncashed replenishment Warrant (Check)
When the petty cash available fund balance is low, a voucher is created in OAKS FIN. The voucher amount is equal to the receipts for the disbursements made from the petty cash. The receipts are the supporting documentation attached to the voucher. This creates a Warrant (Check) that when cashed, restores the petty cash for the disbursements that have been made.
When the account is no longer needed, it is closed by depositing the full authorized amount of the account into the OAKS FIN fund from which it was originally drawn.

Effective July 1, 2016, the Chief Fiscal Officer of a state agency operating an OBM authorized petty cash account(s) is required to sign, and keep current, a Biennial Petty Cash Cetification form acknowledging they will be responsible for administering the petty cash account(s) within their agency in accordance with the responsibilities outlined in the MOU and in this guidance. The MOU will be signed prior to the release of the approved Petty Cash Request form for new petty cash accounts.
The Chief Fiscal Officer shall insure that a petty cash account policy has been established and includes strong internal controls, and processes for performing regular internal reconciliations and the process for disbursement of petty cash funds, replenishment of the account, security of the account, reporting responsibilities, and closure of the account. This is for the purpose of safeguarding the state's assets and reasonably ensuring petty cash transactions are completed accurately and in accordance with State Purchasing guidelines and this guidance.
OBM State Accounting, OBM Office of Internal Audit, or Ohio Auditor of State may, at any time, have access to the petty cash account(s) and related records of any agency. This is for the purpose of verification of the authorized amount and to review that purchases made are in compliance with this guidance and appropriate for the defined use of the account.
Agencies must perform a reconciliation on a regular basis, performed by someone other than the custodian.
What would you like to do?
| Click here to request updates to this topic. |
|